Describe the Inner Lining of the Small Intestine
It absorbs digested food completely. The villi increase the surface area for absorption.
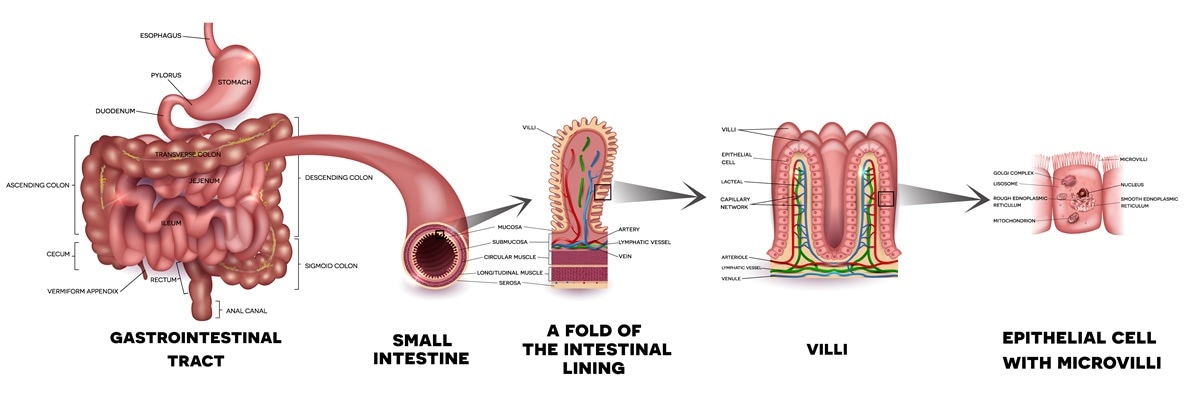
What Does The Small Intestine Do
The lining of the stomach has less surface area than the lining of the small intestine.

. The Lining of the Small Intestine It was long assumed to be a passive tissue. The small intestine is a long highly convoluted tube in the digestive system that absorbs about 90 of the nutrients from the food we eat. The stomach lining has a mucus coating that protects it from acid while the lining of the small intestine is.
The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine that the stomach feeds into. The small intestine is part of the digestive system and is mainly responsible for the absorption of nutrients. These structures greatly increase the area of.
Each villus is covered by a single layer of epithelium and contains blood vessels and lymph vessel. 207 Small intestine Muscularis Externa View Virtual EM Slide Study the orientation of the smooth muscle cells in the intestinal muscularis externa. However underneath the microscope it is a lighter pink with a yellowish tinge.
The micrograph will help you understand the pattern which arises from the inner circular layer and outer longitudinal layer of smooth muscle cells. The mesentery refers to the part of the peritoneum that is responsible for connecting portions of the small intestine to the abdominal wall. Functionally the small intestine is chiefly involved in the digestion and absorption of nutrients.
It is given the name small intestine because it is only 1 inch in diameter making it less than half the diameter of the large intestine. The small intestine is divided into three parts. These folds and projections increase the surface area available for absorption.
In histology an intestinal cryptcalled the crypt of Lieberkühnis a gland found in the epithelial lining of the small intestine and colon. Goblet cells that secrete mucus and enterocytes that secrete water and electrolytes. Enlarged twisted varicose vein in the rectal region.
Chief cellsLocated primarily in the basal regions of gastric glands are chief cells which secrete pepsinogen the inactive proenzyme form of pepsin. The small intestine has a ridged lining covered with tiny fingerlike projections called villi. Its a short descending chute about 10 inches long.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. The jejunum is the middle section of the small intestine. It has a lining which is designed to absorb carbohydrates and proteins.
The inner lining of the stomach as viewed by the eye appears to be a dull pink--almost brown. Recent work has shown that the cells of the lining are covered by a membrane that actively digests foods and speeds nutrients into the blood Nutrients appear to enter the body through the mouth but in a more profound sense nothing becomes part of the body until it has. The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous fingers like projections for villi which increase the.
The crypts and intestinal villi are covered by epithelium that contains two types of cells. It secretes intestinal juice. What is the name of the portion of the stomach closest to the small intestine.
Wall of the small intestine contains numerous gland that secretes intestinal juices containing amylolytic proteolytic lipolytic enzymes for the complete edition of Carbohydrate protein and fat. Imagine cutting a strand of your hair lengthwise. Its this delicate lining that protects you from billions of microbes circulating in your intestines.
It is a very narrow tube with a large internal surface area. The Small Intestinal Lining is one cell layer thick. The mucus lining your stomach helps prevent your stomach lining from the acid Intrinsic factor is a glycoprotein necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestine.
The small intestine is an organ located in the gastrointestinal tract between the stomach and the large intestine. H Describe the appearance of the inner lining of the stomach. Villi increase the surface area of the ileum which facilitates absorption of digested food.
The inner lining of esophagus structurally. How long is the large intestine. The mucous membrane lining the intestinal wall of the small intestine is thrown into transverse folds called plicae circulares and in higher vertebrates minute fingerlike projections known as villi project into the cavity.
The main function of the small intestine is absorption of nutrients and minerals from food. It receives bile juice from the liver and pancreatic juice from the pancreas. Who are the experts.
The inner surface of the jejunum its mucous membrane is covered in projections called villi which increase the surface area of tissue available to absorb nutrients from the gut contents. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. Lack or loss of appetite resulting in the inability to eat.
This is how THIN your lining is. This double-layered membrane is located between the parietal peritoneum that lines the abdominal cavity and the visceral peritoneum that surrounds the digestive organs. Villi are small finger-like projections on the inner lining of the ileum.
What are the different parts of the small intestine. Each villus contains a terminal lymphatic capillary called a lacteal. Learn about the structure of.
Describe the anatomy of the intestinal mucosa. Secretions from the liver and pancreas enter the intestine to help in the digestion process. The small intestine is the part of the intestines where 90 of the digestion and absorption of food occurs the other 10 taking place in the stomach and large intestine.
Up to 24 cash back The pancreas is a bumpy and creamy tan coloured organ underneath the stomach and intestines. Functions of Small Intestine. Protrusion of any organ or structure through the wall of the cavity in which it is naturally contained.
It is on average 23ft long and is comprised of three structural parts. The duodenum jejunum and ileum. The inner lining of the small intestine contains numerous finger like projections called villi.
Describe the specific structural and functional differences in the inner lining of the esophagus stomach small intestine and large intestine. This lining starts from your sinus all way down to rectum. It is the site of complete digestion in humans.
The ileum is the last and longest section of. Condition in which small blisterlike pockets develop in the inner lining of the large intestine. What cell type constitutes the inner lining of the mucosa near the small intestine.
Digestion involves two distinct parts. Answered by Sivanand Patnaik 27th Aug 2018 1054. The intestinal mucosa has transverse folds called circular folds that have small projections called intestinal villi.

Microscopic Colitis Collagenous Colitis And Lymphocytic Colitis Microscopic Colitis Colitis Celiac Disease

A Fold Of The Intestinal Lining Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock

Villi In The Small Intestine Human Digestive System Intestines Intestines Anatomy
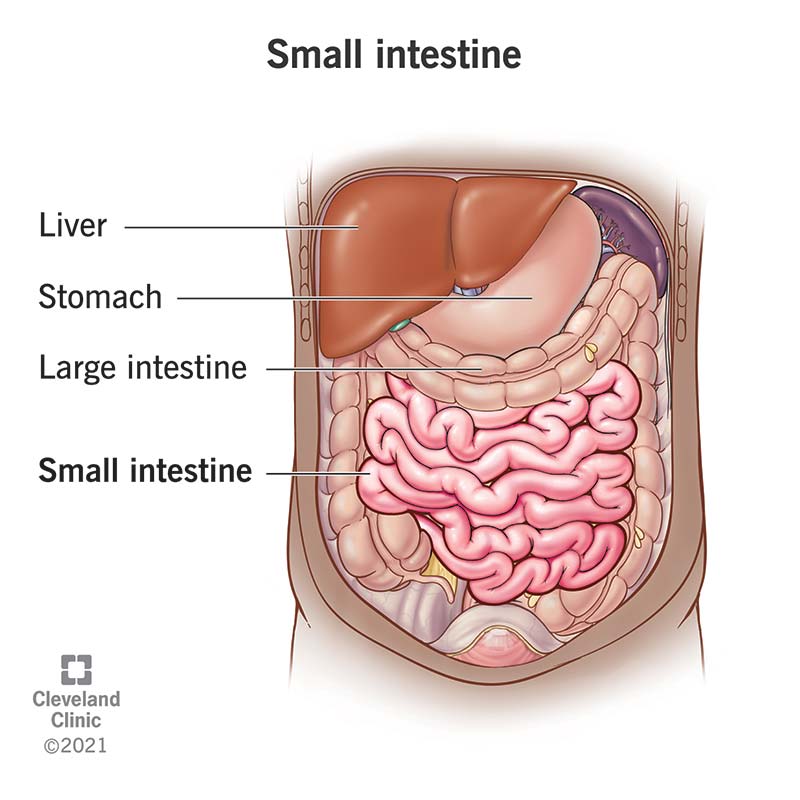
Small Intestine Function Anatomy Definition

Small Intestine Appearance In Celiac Disease Celiac Disease Celiac Disease
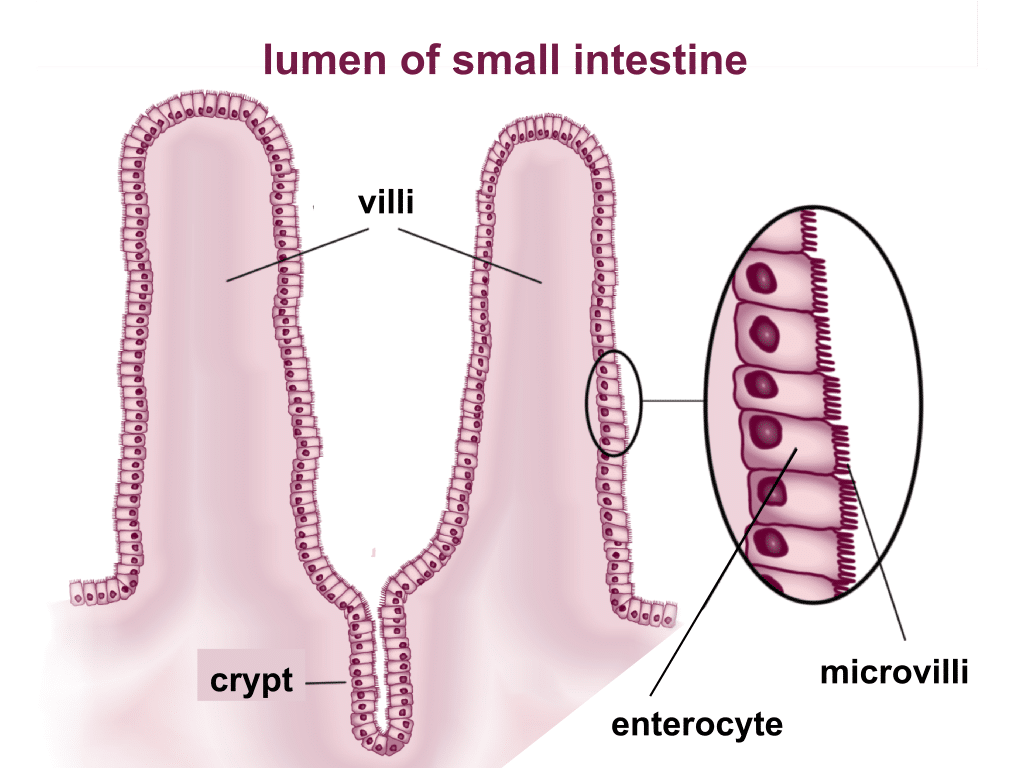
Small Intestine Structure Histology Secretions Teachmephysiology

The Attack This Assault Is Aimed At Your Villi Tiny Finger Like Projections On The Inner Lining Of Your Small Celiac Disease Symptoms Disease Symptoms Celiac

Small Intestine Villi Section Photographic Print Thomas Deerinck Art Com Macro And Micro Things Under A Microscope Intestines
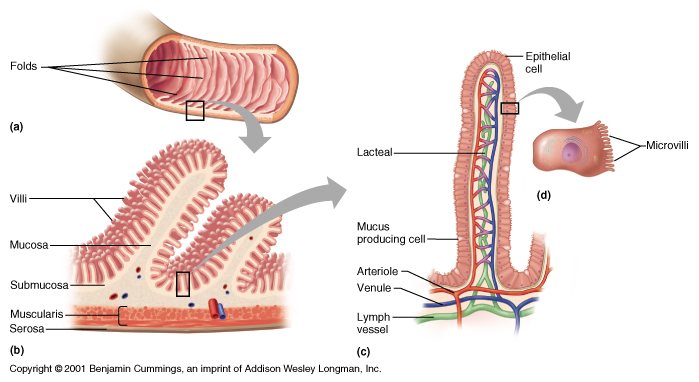
Why Does The Wall Of The Small Intestine Need A Large Surface Area Socratic

The Inner Lining Mucosa Consists Of An Inner Epithelium A Loose Connective Tissue Layer Lamina Propria And A Thin Layer Of Smooth Muscle Muscularis Mucosa

Absorptive Surface Of The Small Intestine Digestive System Anatomy Human Body Anatomy Tissue Biology
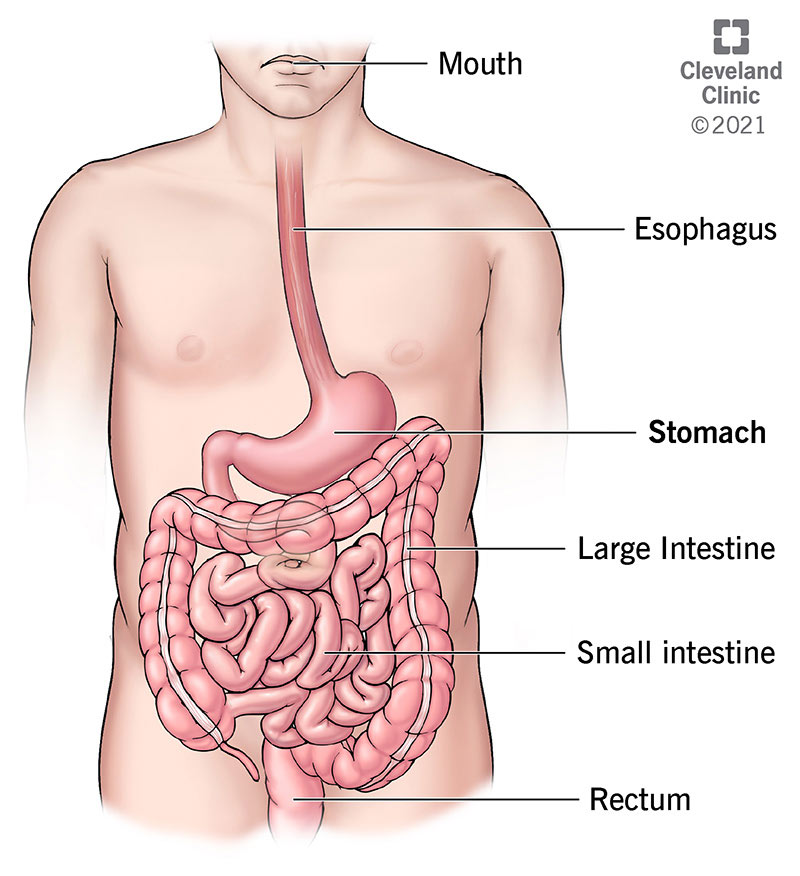
Stomach Anatomy Function Diagram Parts Of Structure

Coloured Sem Of Villi In The Small Intestine Systems Biology Complex Systems Scanning Electron Micrograph

Small Intestine Histology Labeled Google Search Stomach Anatomy And Physiology Plexus Products



Comments
Post a Comment